|
GET
TO KNOW RES
|
|
Can you imagine life without television, cars, or computers? What if you had to cook your dinner over a fire or fetch water from a river? It might be fun for a camping trip, but you probably would not want to do it every day. But that's how life was before scientists and inventors discovered ways to use energy to make our lives easier. Today, most of the energy we use comes from fossil fuels. Coal, oil, and natural gas are all fossil fuels. Over millions of years, the decay of plants, dinosaurs, and other animals was formed into fossil fuels. These fuels lie buried between layers of earth and rock. The only way to get them out is to drill or mine for them. While fossil fuels are still being created today by underground heat and pressure, they are being consumed more rapidly than they are created. For that reason, fossil fuels are considered nonrenewable; that is, they are not replaced as soon as we use them. So, we could run out of them sometime in the future. Or, we might someday use so much fossil fuel that we won't be able to drill or mine fast enough to keep up with the demand. Because our world depends so much
on energy, we need to find sources of energy that will last a
long time. What if there was a type of energy that never ran out?
There is. It is called renewable energy.
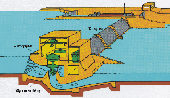
What is renewable energy? Renewable energy systems use resources that are constantly replaced and are usually less polluting. Examples of renewable energy systems include solar, wind, and geothermal energy (getting energy from the heat in the earth). We also get renewable energy from trees and plants, rivers, and even garbage. Wind power Hydropower
However, the drawback to hydropower is that damming rivers can change the ecology of the region. For example, the water below the dam is often colder than what would normally flow down the river, so fish sometimes die. The water level of the river below the dam can be higher or lower than its natural state, which affects the plants that grow along the riverbanks. Biomass energy There are three ways to use biomass. It can be burned to produce heat and electricity, changed to a gas-like fuel such as methane, or changed to a liquid fuel. Liquid fuels, also called biofuels, include two forms of alcohol: ethanol and methanol. Because biomass can be changed directly into a liquid fuel, it could someday supply much of our transportation fuel needs for cars, trucks, buses, airplanes, and trains. Solar energy Geothermal
energy Energy from wastes Garbage is also an inexpensive energy resource. Unlike most other energy resources, someone will collect garbage, deliver it to the power plant, and pay to get rid of it. This helps cover the cost of turning the garbage into energy. Garbage is also a unique resource because we all contribute to it. Renewable
energy in your future Source:
|
|
ALSO
READ :
|
|
Glossary
for Renewable Energy Sources |

Wind Turbine
Hydropower Plant
Biomass

Solar Element
Images:
webpage
http://chania.chania.teiher.gr/ppe53